PPI: Health Prices Remain Tame
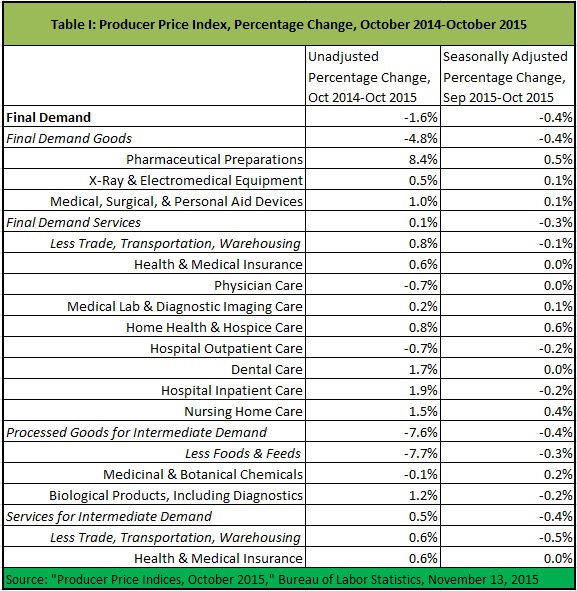
 Although I did not discuss June’s release of the Producer Price Index (PPI) for May at this blog (due to vacation), prices of pharmaceutical preparations did not increase at all. Similarly, they remained flat in today’s PPI release for June.
Although I did not discuss June’s release of the Producer Price Index (PPI) for May at this blog (due to vacation), prices of pharmaceutical preparations did not increase at all. Similarly, they remained flat in today’s PPI release for June.
Prices for final demand goods (less food and energy), and prices for all final demand health services were either flat or down in June. Similarly, price changes of health services for final demand were all lower than price changes for final demand services overall. The same was true for both goods and services for intermediate demand.
For the last 12 months, prices of health goods and services (especially pharmaceutical preparations) have increased significantly more than prices of other goods and services, but the trend of disproportionately high health price increases might be breaking down.
(See Table I below the fold.)